C2v81 MW mic8 Projection, Stuart tonal distinction 5.
| Stuart C2v81 M19(STU) MW mic8.wav |
Steinway C2v81 STE MW mic8.wav |
| Sound table 4.38 | |
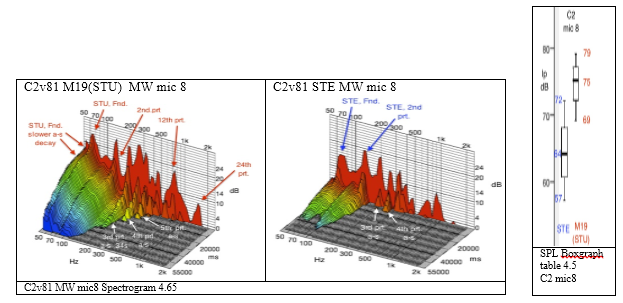
C2v81, sounded 9dB louder than Steinway at 6 metres. The slower velocity strikes of C2 produced wider contrasts in SPL.12dB for v20 and 11dB for v54. The box graph shows the exact dB levels of the 6 notes.
The Stuart produced a more complete harmonic spectrum, as illustrated in the spectrogram below, with a significantly larger fundamental, 2nd, 3rd, 4th , and 5th partial frequencies.
The Stuart fundamental frequency rate of decay slowed significantly more than Steinway in its after-sound.
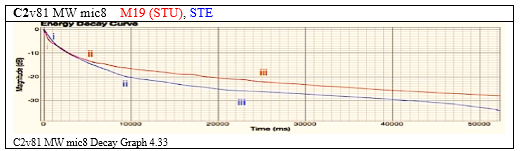
The decay curves below, show the Stuart (i) to be decaying faster in the onset, and to be settling into its after-sound oscillation (ii) , approximately 5s earlier than Steinway (ii).
Soundboard: The Stuart soundboard vibrated larger harmonic vibrations than Steinway by 47% , for C2v81. The Spectrum of the Stuart s-board was wider, with strong vibrations of the Fundamental to the 13th partial frequency. The Steinway didn’t vibrate higher than the 9th partial, and vibrated a larger fundamental frequency than Stuart.
String scale: The C2 string diameter of the Paulello/Stuart core wire is .125mm thicker, the cover wire is .47mm thicker and Stainless Steel, the tensile strength of the Paulello/Stuart wire is 481 N/mm² higher, the Paulello/Stuart is 235mm longer, and is set at 65.3kg higher tension. The yield or capacity of the Paulello/Stuart. wire is 46% higher than Paulello/Stuart.
C2 v81 exhibited the three distinctive characteristics of the Stuart sound found in previous tests, slower decay in the fundamental, a wider spectrum and earlier entry into the after-sound oscillation.




